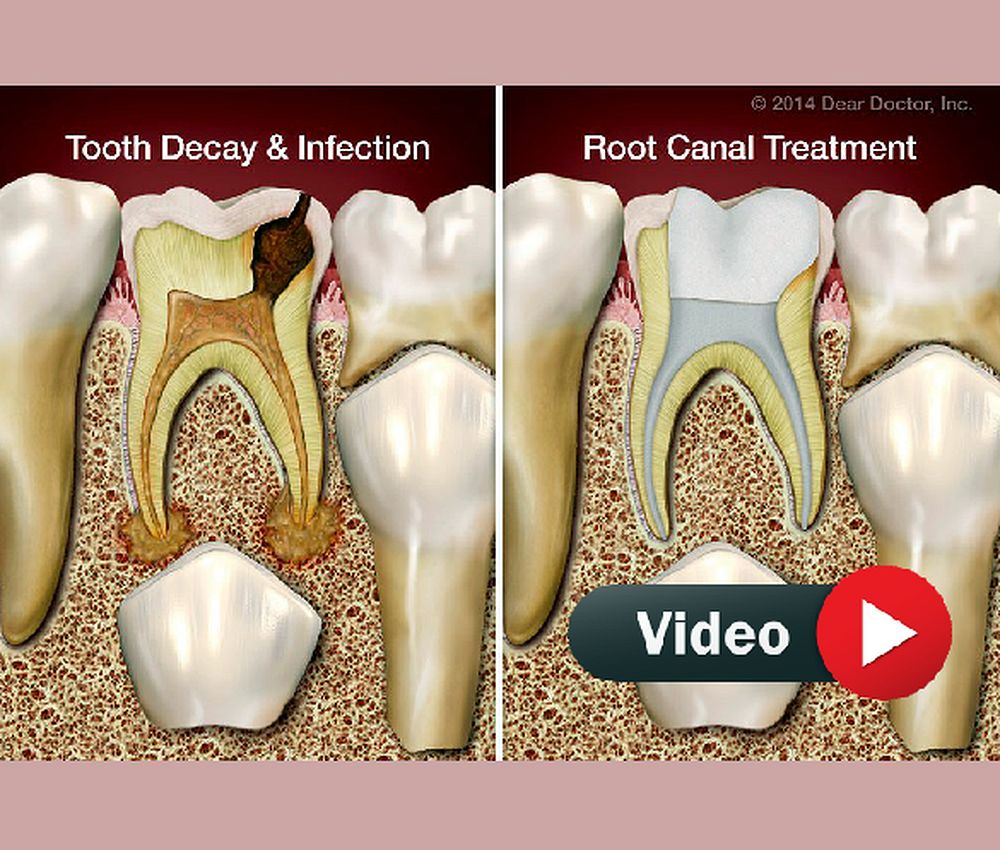
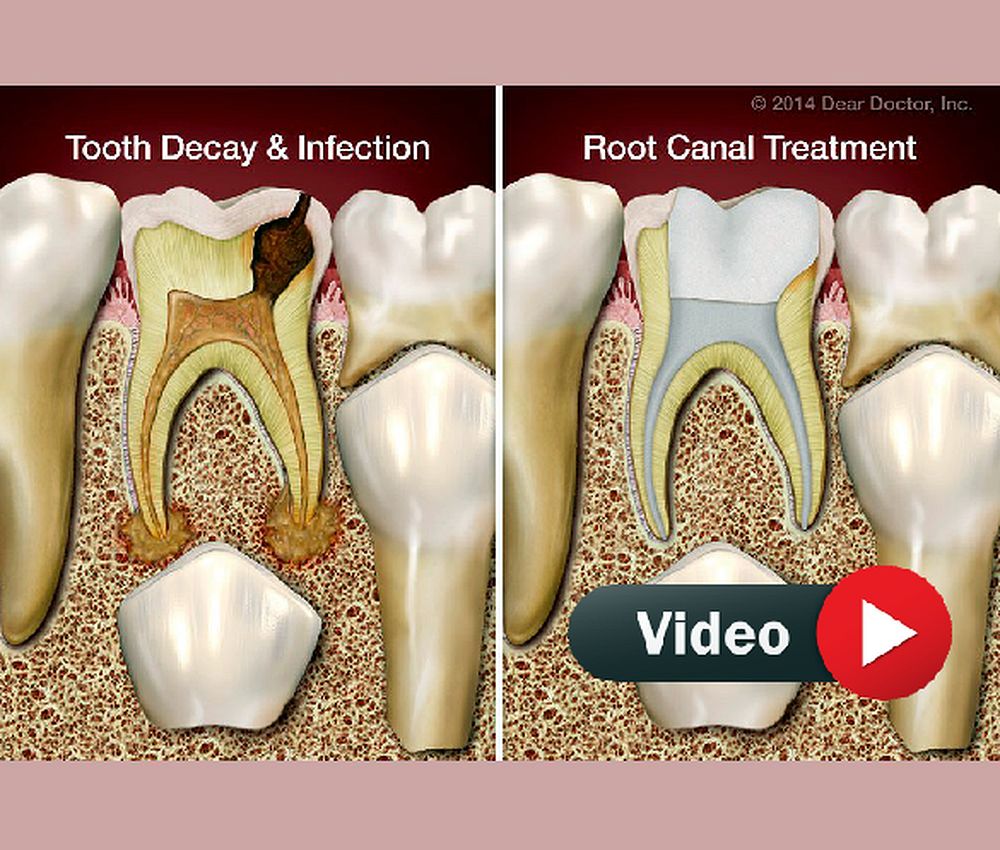
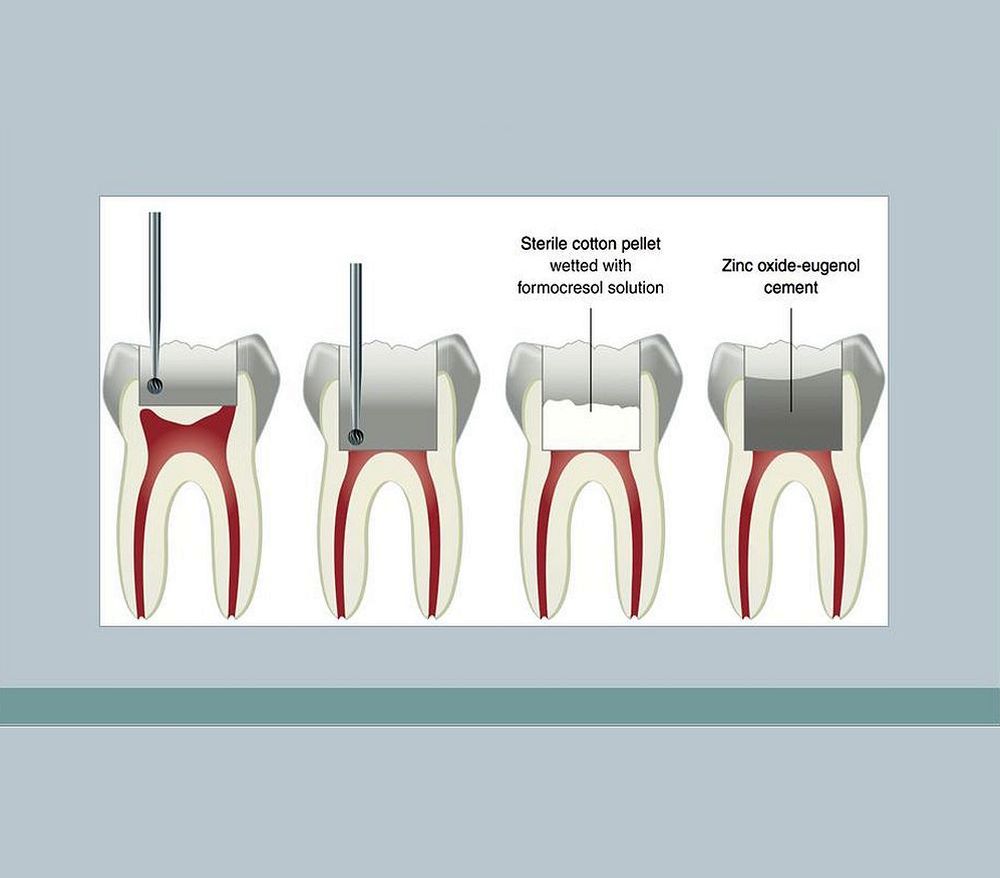
Pulp therapy in primary teeth is a cornerstone of pediatric dentistry, aiming to maintain tooth vitality, prevent infection, and preserve arch space until natural exfoliation.
📌 Recommended Article :
Dental Article 🔽 Why Hydrogen Peroxide Should Not Be Used in Modern Endodontic Treatment: Evidence-Based Clinical Justification ... This article explains why hydrogen peroxide is no longer recommended in endodontic treatments, supported by contemporary scientific evidence.Advances in biomaterials such as MTA, Biodentine, and improved clinical protocols have significantly increased success rates. Understanding the differences between pulpotomy, pulpectomy, indirect pulp treatment (IPT), and apexification is essential for evidence-based care.
Advertisement
✅ Pulp Therapy Techniques
➤ Indirect Pulp Treatment (IPT)
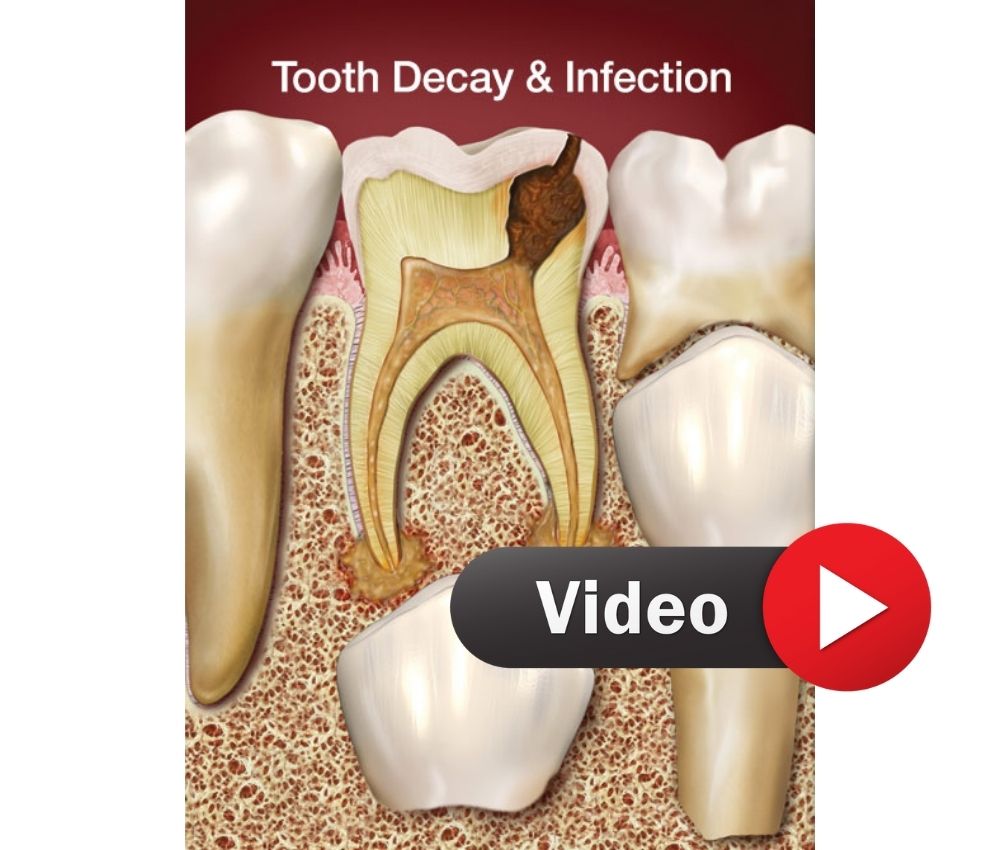
IPT is indicated when deep caries is present but the tooth remains vital and asymptomatic. Selective caries removal minimizes pulp exposure and promotes remineralization. High-fluoride glass ionomer and resin-modified glass ionomer (RMGI) are widely used as liners.
➤ Direct Pulp Cap (DPC)
Used when a small mechanical pulp exposure occurs. Bioceramics like MTA and Biodentine create a durable dentin bridge and exhibit excellent biocompatibility.
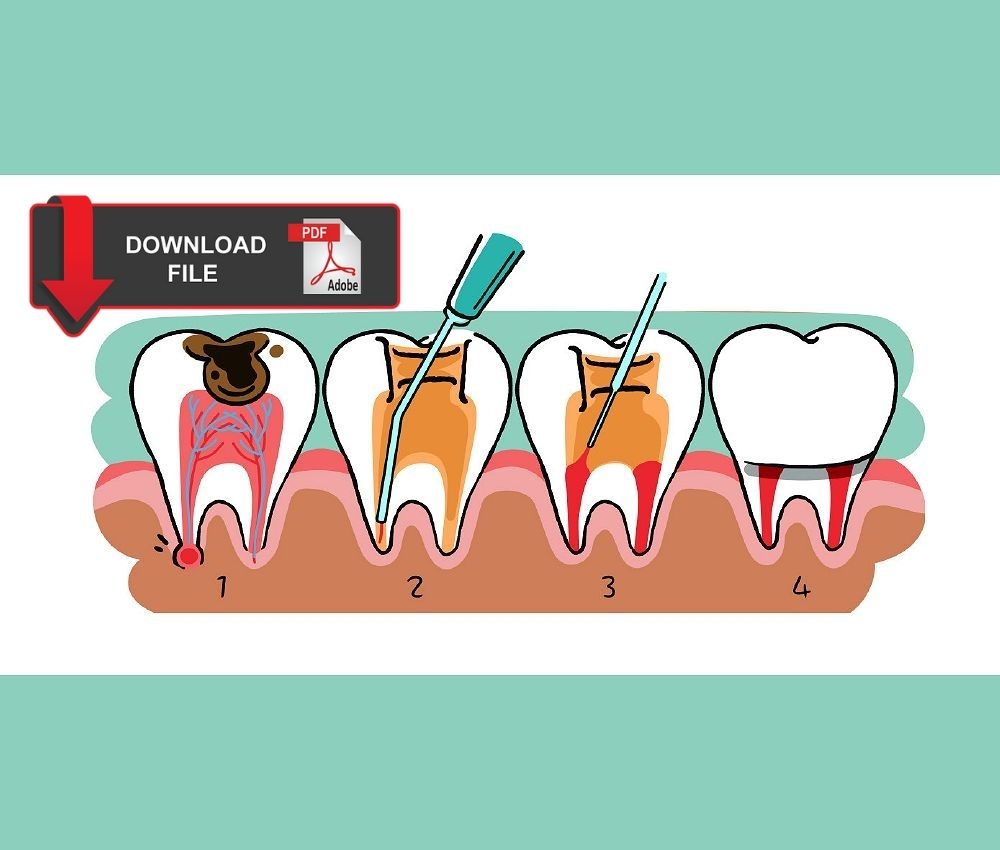
➤ Pulpotomy
Indicated in cases of carious pulp exposure with preserved radicular pulp vitality. Popular medicaments include MTA, Biodentine, and historically formocresol, although the latter is no longer recommended due to toxicity concerns.
➤ Pulpectomy
Indicated for irreversible pulpitis or necrosis. It consists of removing necrotic tissue and obturating canals with resorbable materials such as iodoform-based pastes (Vitapex, Metapex) or zinc oxide–eugenol.
➤ Apexogenesis & Apexification in Young Permanent Teeth
Although not used in primary teeth, they are fundamental when treating immature permanent teeth with open apices.
📌 Recommended Article :
Dental Article 🔽 Understanding Pulpal Diseases: Reversible Pulpitis, Irreversible Pulpitis, and Pulp Necrosis in Adults and Children ... Pulpal diseases represent a continuum of inflammatory conditions that range from reversible pulpitis to irreversible pulpitis and finally to pulp necrosis.✅ Materials Used in Pulp Therapy
➤ Mineral Trioxide Aggregate (MTA)
Known for high biocompatibility, antibacterial properties, and superior long-term sealing.
➤ Biodentine
A bioactive dentin substitute with faster setting time and strong pulpal healing potential.
➤ Zinc Oxide–Eugenol (ZOE)
Traditional obturation material for primary teeth, but less favorable in cases requiring complete resorption.
➤ Iodoform-based Pastes (Vitapex/Metapex)
Preferred for pulpectomy due to their resorbability and antimicrobial action.
📌 Recommended Article :
Dental Article 🔽 Calcium Hydroxide in Pediatric Dentistry: Benefits and Limitations ... Its biological properties, high alkalinity, and ability to stimulate hard tissue formation have made it a cornerstone in pulp therapy procedures.✅ Success Rates
▪️ IPT: 90–97% (AAPD, 2021)
▪️ Pulpotomy with MTA: 90–95%
▪️ Pulpotomy with Biodentine: 88–94%
▪️ Pulpectomy: 70–85%, depending on canal anatomy and material used
📊 Comparative Table: Differences Between Pulp Therapy Techniques
| Aspect | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Indirect Pulp Treatment (IPT) | High success rates; preserves vitality; minimally invasive | Requires excellent diagnosis; risk of residual caries |
| Direct Pulp Cap (DPC) | Promotes dentin bridge formation; effective with bioceramics | Not suitable for carious exposures; requires ideal isolation |
| Pulpotomy | High success with MTA/Biodentine; preserves radicular pulp vitality | Failure if radicular pulp is inflamed or infected |
| Pulpectomy | Indicated for necrotic teeth; removes infection; allows tooth preservation | Technique sensitive; lower success rates; requires resorbable obturants |
| Apexogenesis | Allows continued root development | Not applicable to primary teeth |
| Apexification | Induces apical closure in young permanent teeth | Long treatment time; not used in primary teeth |
The choice of pulp therapy depends on diagnosis, degree of inflammation, tooth restorability, and patient behavior. Vital pulp therapies (IPT, DPC, pulpotomy) consistently show higher long-term success than pulpectomy. Modern biomaterials like MTA and Biodentine have replaced older agents due to improved healing outcomes and safety profiles.
📌 Recommended Article :
Dental Article 🔽 Medications for Pulp Capping in Primary Teeth: Indications, Composition, and Clinical Management ... Its success largely depends on the material or medication used, which must be biocompatible, promote tissue repair, and provide an adequate marginal seal.🔎 Recommendations
▪️ Prioritize vital pulp therapies when pulp vitality is preserved.
▪️ Use bioceramics (MTA, Biodentine) as first-line agents.
▪️ Perform pulpectomy only when irreversible pulpitis or necrosis is confirmed.
▪️ Seal treated teeth with stainless steel crowns for long-term success.
▪️ Follow AAPD guidelines for diagnostic criteria and material selection.
✍️ Conclusion
Pulp therapy in primary teeth is highly successful when clinicians use accurate diagnostic criteria and evidence-based materials. Modern biomaterials have improved outcomes and reduced complications, making pulp conservation the preferred approach whenever possible. A clear understanding of each technique ensures predictable and biologically sound results.
📚 References
✔ American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry. (2021). Pulp therapy for primary and immature permanent teeth. AAPD Clinical Guidelines. https://www.aapd.org
✔ Hegde, S., & Bhat, S. S. (2019). Clinical evaluation of MTA and Biodentine as pulpotomy agents in primary teeth. Journal of Indian Society of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry, 37(3), 307–315. https://doi.org/10.4103/JISPPD.JISPPD_217_18
✔ Jeon, H. J., Kim, J., & Kim, Y. (2020). Outcomes of vital pulp therapy using bioceramic materials. Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics, 45(3), e32. https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e32
✔ Nowicka, A., Lipski, M., Parafiniuk, M., et al. (2013). Biodentine vs. MTA in direct pulp capping. Journal of Endodontics, 39(6), 743–747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2013.01.005
📌 More Recommended Items
► Best Materials for Pulpotomy in Primary Teeth: MTA vs. Biodentine vs. Ferric Sulfate
► Pulp Capping in Dentistry: How the Dental Pulp Is Protected (Updated Clinical Guide)
► CTZ Paste in Primary Teeth Pulp Therapy: Indications, Benefits and Clinical Protocol