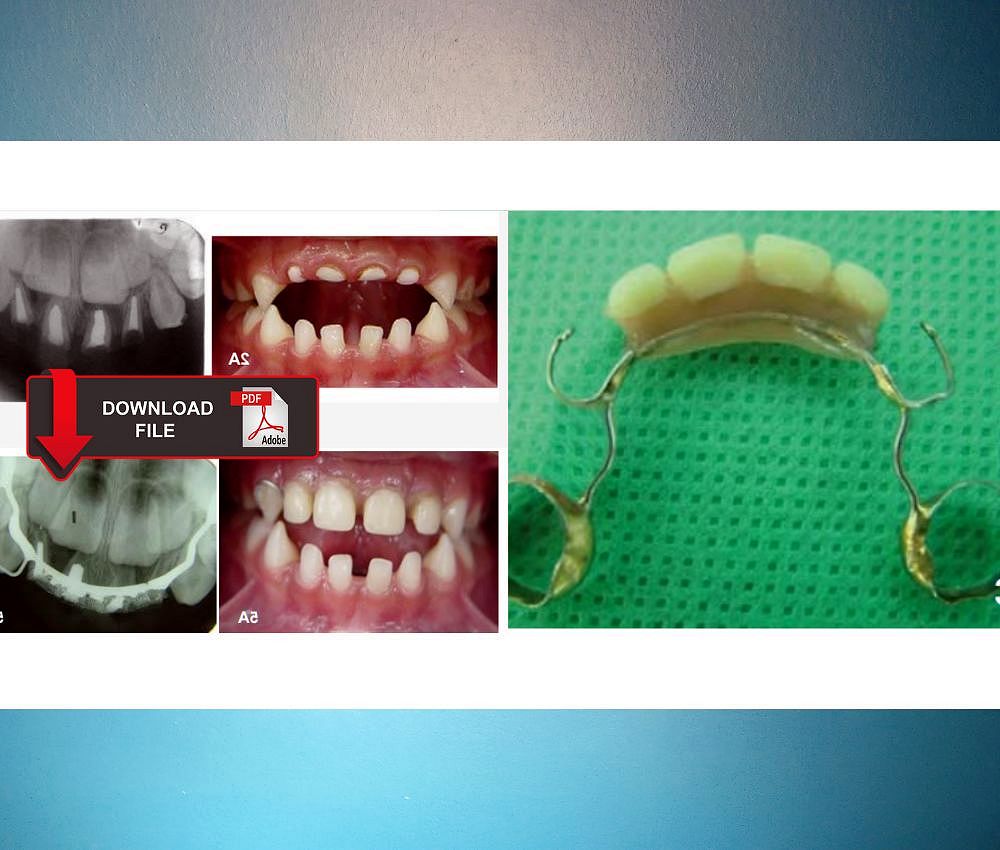
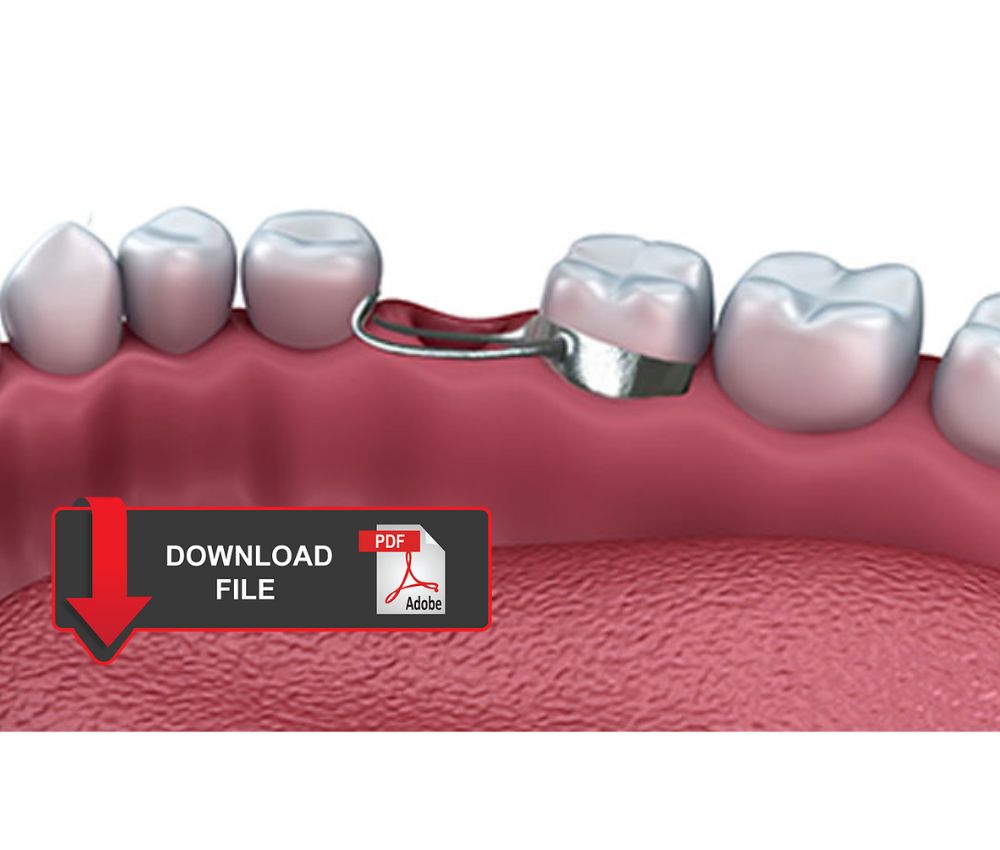
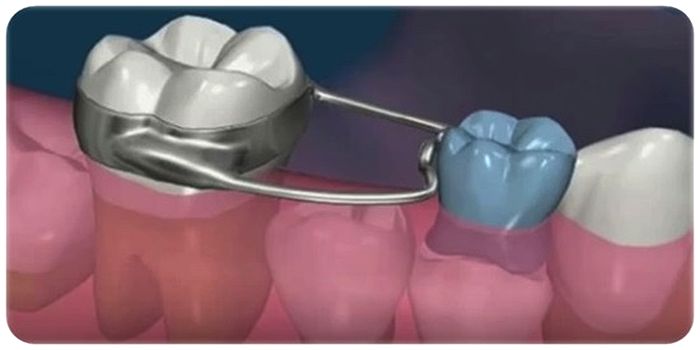
Interceptive orthodontics refers to early orthodontic intervention performed during the mixed dentition stage to eliminate or reduce the severity of developing malocclusions. Its goal is to intercept abnormal growth patterns and dental discrepancies before they become severe.
📌 Recommended Article :
PDF 🔽 Space Maintainers: Types, indications and complications ... Space maintainers can be fixed or removable, unilateral or bilateral, and have different designs. The specialist will decide which type of maintainer is suitable for the patient after a clinical and radiographic evaluation.Interceptive orthodontics does not replace comprehensive orthodontic treatment, but it significantly simplifies future therapy.
Advertisement
✅ Justification
Early orthodontic problems can worsen if left untreated. Interceptive orthodontics is justified because it:
▪️ Takes advantage of active craniofacial growth
▪️ Reduces the need for extractions or surgery later
▪️ Improves esthetics, function, and psychosocial well-being
▪️ Prevents trauma to protruding incisors
Timely intervention can modify unfavorable growth patterns, which is not possible once growth is complete.
📌 Recommended Article :
Dental Article 🔽 Maxillary Orthopedics vs. Interceptive Orthodontics: Understanding Their Clinical Differences ... This article explores their definitions, characteristics, objectives, and the most common appliances used in each approach.✅ Objectives of Interceptive Orthodontics
The main objectives include:
▪️ Guiding proper jaw growth
▪️ Correcting developing malocclusions
▪️ Eliminating harmful oral habits
▪️ Creating space for permanent teeth eruption
▪️ Reducing treatment complexity in adolescence
The primary focus is prevention rather than correction.
📌 Recommended Article :
Dental Article 🔽 Bionator Appliance: Objectives, Indications, Advantages and Disadvantages ... The Bionator appliance is introduced as a key functional device in early orthopedic treatment, guiding jaw growth and improving the balance between oral structures during a child’s developmental years.✅ Most Representative Appliances
Commonly used interceptive orthodontic appliances include:
▪️ Space maintainers
▪️ Palatal expanders
▪️ Lingual holding arches
▪️ Removable active plates
▪️ Habit-breaking appliances
▪️ Functional appliances (e.g., activators, Frankel appliances)
Appliance selection depends on growth stage, diagnosis, and patient cooperation.
📌 Recommended Article :
Dental Article 🔽 Do Wisdom Teeth Cause Dental Crowding? Updated Evidence and Clinical Insights ... Wisdom teeth, or third molars, typically erupt between the ages of 17 and 21, coinciding with the period when patients often notice anterior crowding of the mandibular incisors.✅ Until What Age Can Interceptive Orthodontics Be Used?
Interceptive orthodontics is typically indicated:
▪️ Between 6 and 10 years of age
▪️ During early mixed dentition
▪️ While active skeletal growth is present
Its effectiveness decreases significantly after the pubertal growth spurt, when growth modification is limited.
💬 Discussion
There is ongoing debate regarding the timing of orthodontic intervention. While not all malocclusions require early treatment, specific conditions such as crossbites, severe crowding, and skeletal discrepancies benefit greatly from interceptive orthodontics. Evidence supports early intervention when growth modification is feasible and when delaying treatment may worsen prognosis.
Proper case selection is critical to avoid overtreatment.
📊 Comparative Table: Interceptive Orthodontics vs Maxillary Orthopedics
| Aspect | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Interceptive Orthodontics | Prevents worsening of dental malocclusions during growth | Limited effect once skeletal growth is completed |
| Maxillary Orthopedics | Modifies jaw growth and skeletal relationships | Highly dependent on patient age and compliance |
Interceptive orthodontics is a preventive and growth-guided approach that plays a fundamental role in modern pediatric dentistry. By addressing developing malocclusions early, it reduces treatment complexity, improves outcomes, and supports healthy craniofacial development.
📌 Recommended Article :
Dental Article 🔽 How to Correct Harmful Oral Habits in Children That Affect Facial and Dental Development ... Early childhood is a critical period for craniofacial and dental development. Certain harmful oral habits, such as thumb sucking, mouth breathing, or nail biting, can interfere with proper facial growth and tooth alignment.🎯 Clinical Recommendations
▪️ Perform early orthodontic screening by age 6
▪️ Identify skeletal and dental discrepancies promptly
▪️ Use interceptive treatment only when clear benefits outweigh risks
▪️ Educate parents about the preventive nature of early orthodontic care
📚 References
✔ American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry. (2023). Guideline on management of the developing dentition and occlusion. Pediatric Dentistry, 45(6), 292–304.
✔ Proffit, W. R., Fields, H. W., Larson, B., & Sarver, D. M. (2019). Contemporary Orthodontics (6th ed.). Elsevier.
✔ Graber, L. W., Vanarsdall, R. L., Vig, K. W. L., & Huang, G. J. (2017). Orthodontics: Current Principles and Techniques (6th ed.). Elsevier.
✔ Bishara, S. E. (2001). Timing of orthodontic treatment: An overview. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics, 120(3), 241–245. https://doi.org/10.1067/mod.2001.116303
📌 More Recommended Items
► What are impacted canines? - Treatment
► Most Common Oral Habits in Children and Their Impact on Teeth
► Crossbite in Children: Why Early Correction Matters and Which Appliances Are Used