Minimally Invasive Dentistry (MID) represents a modern, evidence-based approach that prioritizes the preservation of healthy dental tissues, early disease detection, and prevention-focused care.
📌 Recommended Article :
PDF 🔽 Fluoride Varnish in the Prevention of Dental Caries in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review ... Fluoride varnish is easy to apply, offers greater absorption of minerals on the teeth, and is very safe, unlike other topical fluoride treatments (gels and rinses).Rather than aggressive operative interventions, MID emphasizes biological respect for tooth structure and long-term oral health outcomes.
Advertisement
✅ Definition of Minimally Invasive Dentistry
Minimally Invasive Dentistry is a philosophy of dental care aimed at preventing disease, detecting pathology at its earliest stage, and using the least invasive treatment possible to restore oral health.
Importantly, MID is not a disease, nor a manifestation of one; instead, it is a clinical and preventive care model applied across multiple dental specialties.
📌 Recommended Article :
Video 🔽 How to Apply: Clinpro Sealant - Step by step ... Dental sealants are flowable resins that are placed in the pits and fissures of teeth (usually molars) to prevent cavities. The sealant is placed when the permanent molars erupt (approximately 6 years).✅ Etiology and Rationale
The emergence of MID is driven by:
▪️ Improved understanding of caries as a dynamic biofilm-mediated disease
▪️ Advances in diagnostic technologies
▪️ Evidence showing that tooth structure does not regenerate
▪️ Recognition that traditional “drill-and-fill” dentistry leads to the restorative cycle and premature tooth loss
📌 Recommended Article :
Video 🔽 Use of Silver Diamine Fluoride (SDF) - General Guide on its application ... Silver diamine fluoride (SDF) is a topical medicine that is used to stop the advance of caries and in cases of dentin hypersensitivity. It can be used in both primary and permanent dentition.✅ Clinical Signs and Symptoms Addressed by MID
Although MID is not a pathology, it targets early clinical findings such as:
▪️ Initial enamel demineralization (white spot lesions)
▪️ Early occlusal or proximal caries
▪️ Non-cavitated lesions
▪️ Dental erosion and abrasion
▪️ Initial dentin hypersensitivity
📌 Recommended Article :
Dental Article 🔽 Latest FDA Guidelines (2025) on Fluoride Use in Children: What Dentists Need to Know ... These updates address long-standing concerns surrounding unapproved systemic fluoride products, raising new questions for pediatric dental practice.✅ Key Characteristics of Minimally Invasive Dentistry
▪️ Early diagnosis and risk assessment
▪️ Emphasis on prevention and remineralization
▪️ Maximum preservation of enamel and dentin
▪️ Use of adhesive and conservative restorative techniques
▪️ Continuous monitoring rather than immediate operative treatment
📌 Recommended Article :
Dental Article 🔽 Xylitol and Dental Caries Prevention in Children: Mechanism, Benefits, and Clinical Use ... This review explores its mechanism of action, clinical indications, dosage in pediatric populations, and how it compares with other caries-preventive agents such as fluoride and sorbitol.✅ Treatments Included in Minimally Invasive Dentistry
Common MID procedures include:
▪️ Caries risk assessment and individualized prevention plans
▪️ Fluoride varnish and remineralization therapies
▪️ Sealants and resin infiltration
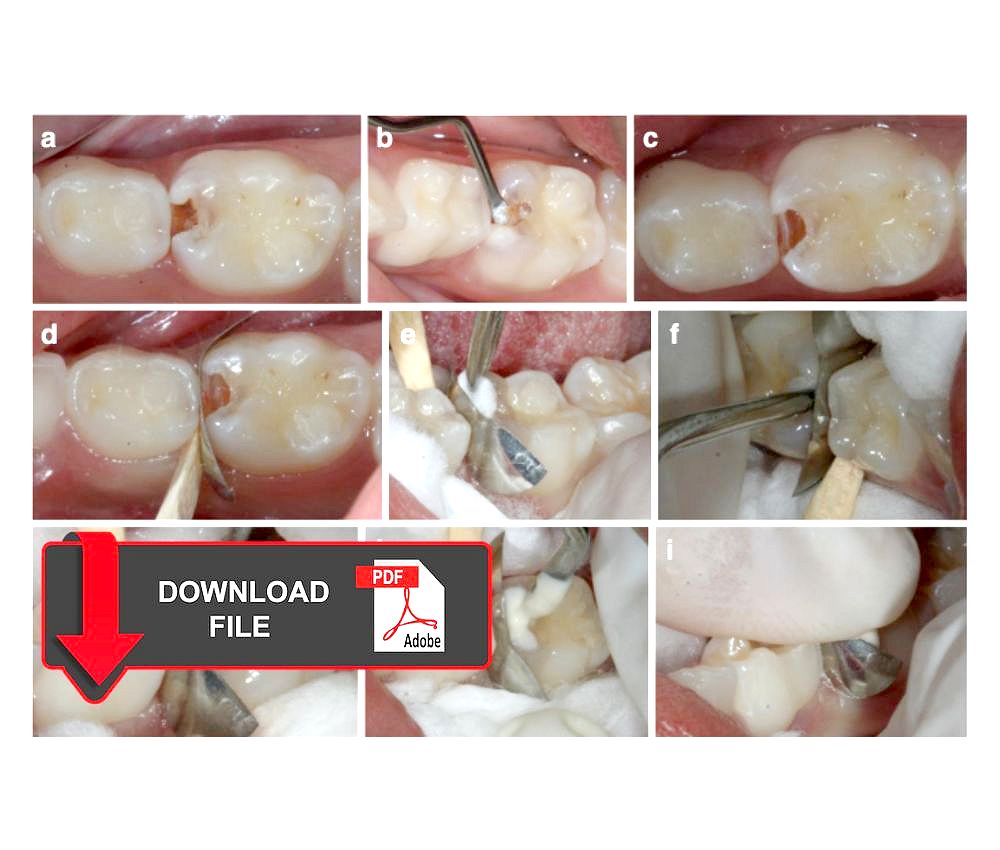
▪️ Atraumatic restorative treatment (ART)
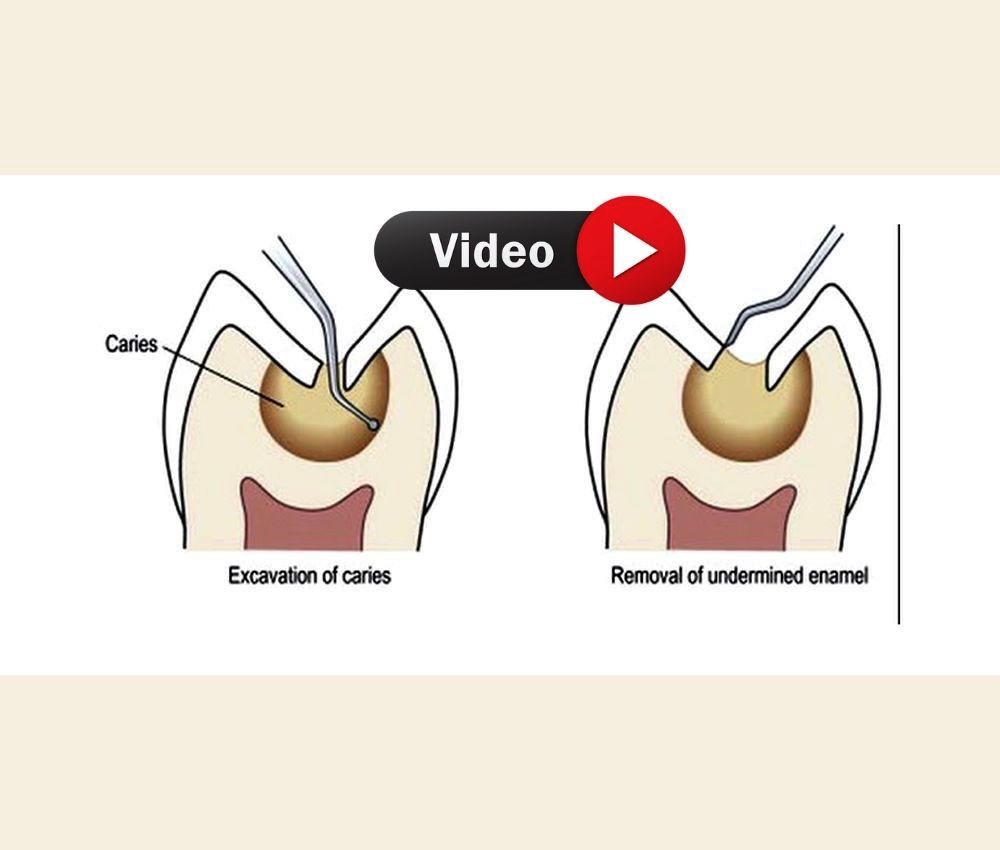
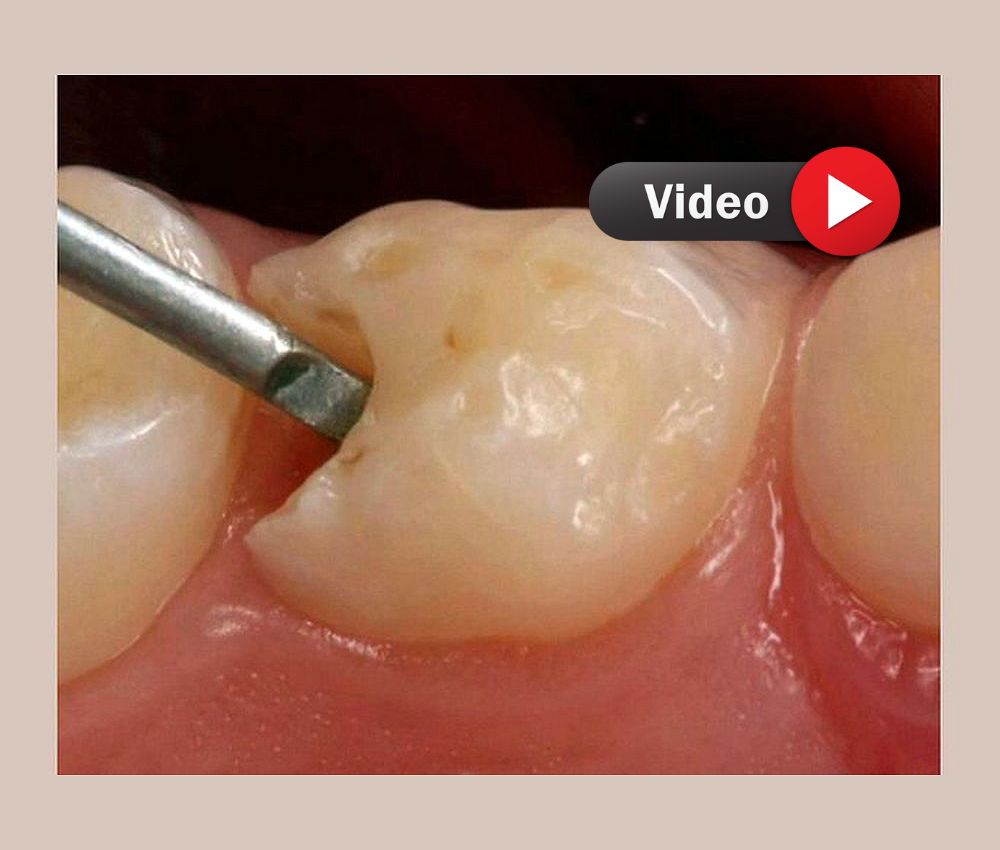
▪️ Selective caries removal
▪️ Preventive resin restorations (PRR)
▪️ Non-invasive management of erosion and sensitivity
📌 Recommended Article :
Dental Article 🔽 Silver Diamine Fluoride in Pediatric Dentistry: A Review ... This review explores its mechanism of action, clinical indications, advantages, and limitations compared to other fluoride therapies used in pediatric dentistry.💬 Discussion
Minimally invasive dentistry shifts the focus from operative intervention to disease control. This paradigm improves patient comfort, reduces anxiety, and enhances long-term tooth survival. However, successful implementation requires accurate diagnosis, patient compliance, and continuous professional education.
Despite its benefits, MID may be underutilized due to outdated clinical habits or limited access to diagnostic technologies in some settings.
🎯 Clinical Recommendations
▪️ Perform individualized caries risk assessments at every recall visit
▪️ Prioritize non-operative treatments for non-cavitated lesions
▪️ Educate patients on diet, oral hygiene, and fluoride use
▪️ Use restorative intervention only when cavitation or structural compromise is present
▪️ Monitor lesions longitudinally using standardized criteria
✍️ Conclusion
Minimally Invasive Dentistry is a cornerstone of modern dental practice, offering a scientifically supported, patient-centered approach that preserves natural tooth structure and promotes long-term oral health. Its integration into daily practice represents a critical step toward sustainable and ethical dental care.
📊 Comparative Table: Minimally Invasive Techniques in Pediatric and General Dentistry
| Aspect | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Atraumatic Restorative Treatment (Pediatric Dentistry) | No drilling, minimal discomfort, ideal for young or anxious children | Limited durability in high caries risk cases |
| Silver diamine fluoride – SDF (Pediatric Dentistry) | Effective caries arrest without anesthesia or tooth preparation | Permanent black staining of carious tissue |
| Pit and fissure sealants (Both) | Highly effective in preventing occlusal caries | Technique-sensitive and requires periodic evaluation |
| Selective caries removal (Both) | Preserves pulp vitality and healthy tooth structure | Requires accurate diagnosis and strict case selection |
| Resin infiltration (General Dentistry) | Arrests early enamel lesions without cavity preparation | Limited to non-cavitated lesions |
| Preventive resin restorations – PRR (General Dentistry) | Combines minimal excavation with preventive sealing | Not indicated for extensive dentinal caries |
| Adhesive restorative techniques (General Dentistry) | Conserves enamel and dentin while providing strong bonding | Technique-sensitive and moisture dependent |
✔ Frencken, J. E., Peters, M. C., Manton, D. J., Leal, S. C., Gordan, V. V., & Eden, E. (2012). Minimal intervention dentistry for managing dental caries – A review. International Dental Journal, 62(5), 223–243. https://doi.org/10.1111/idj.12007
✔ Tyas, M. J., Anusavice, K. J., Frencken, J. E., & Mount, G. J. (2000). Minimal intervention dentistry—a review. FDI World Dental Federation, International Dental Journal, 50(1), 1–12.
✔ Innes, N. P. T., Chu, C. H., Fontana, M., Lo, E. C. M., Thomson, W. M., Uribe, S., … Schwendicke, F. (2019). A century of change towards prevention and minimal intervention in cariology. Journal of Dental Research, 98(6), 611–617. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034519837252
📌 More Recommended Items
► Webinar: Minimally Invasive Dentistry - Dra. Aisha Mohamed
► Minimally Invasive Pediatric Dentistry: Hall Technique, SMART, and ART — A Clinical Guide for Parents and Practitioners
► Webinar: The SMART pediatric dentistry: Minimally Invasive Restorative Techniques - Dra. Jeanette MacLean




.jpg)