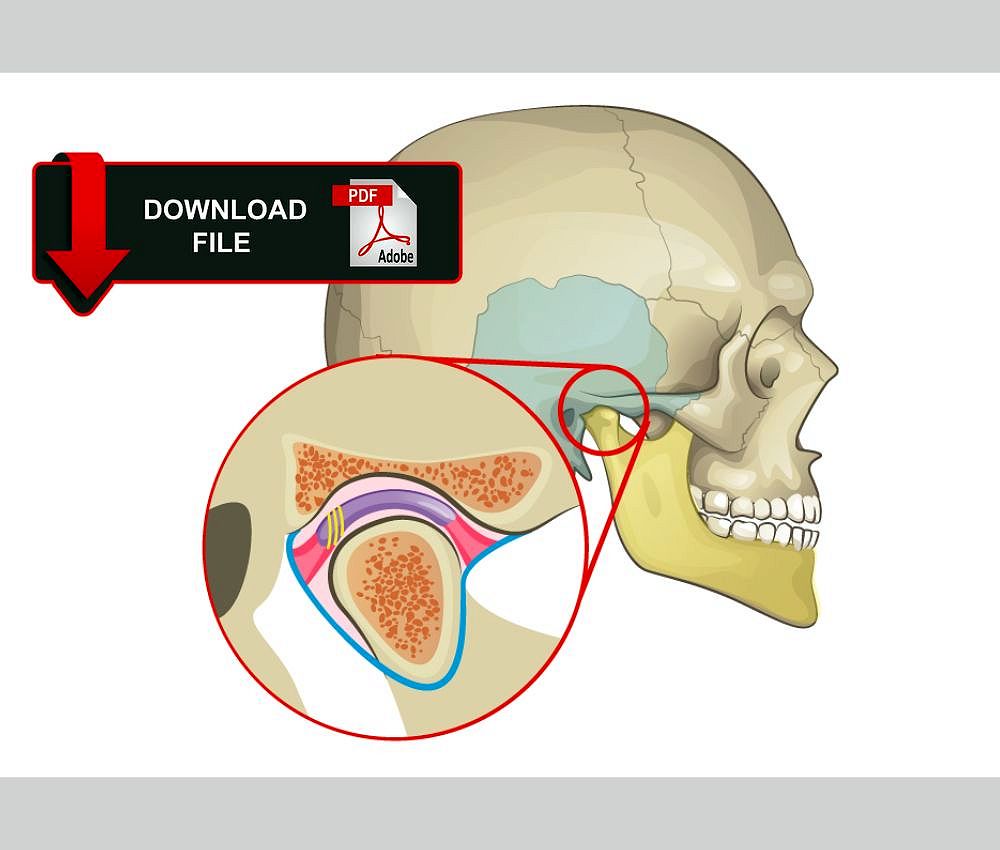
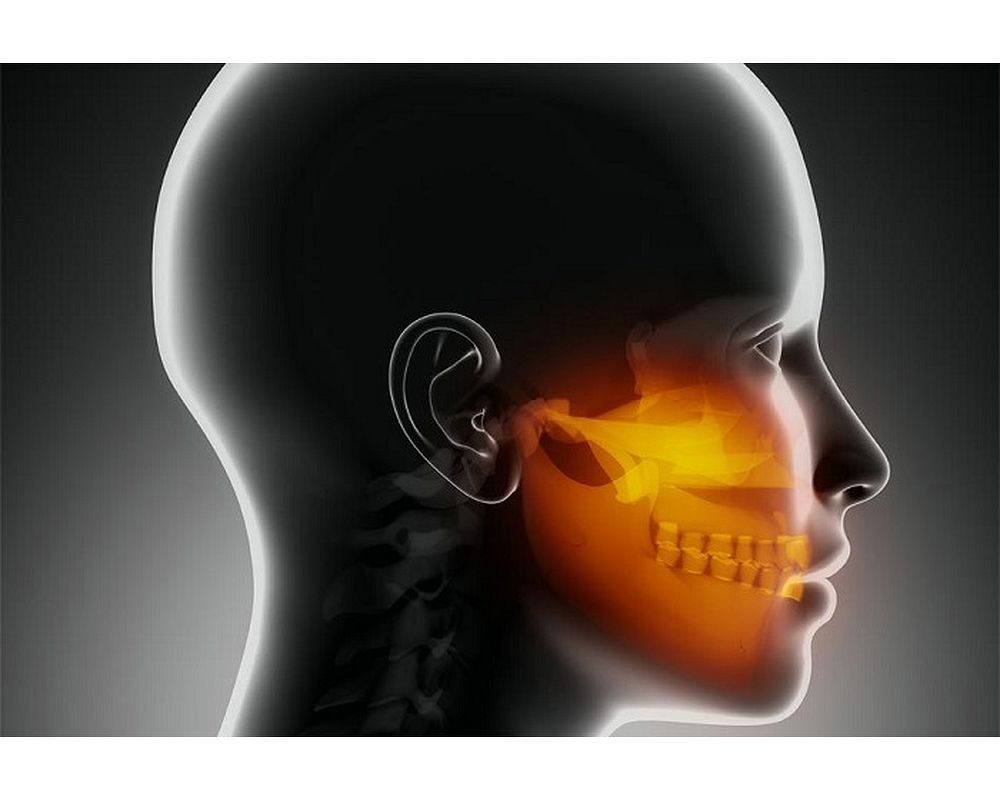
Temporomandibular disorders (TMD) in pediatric patients are increasingly recognized as a significant cause of orofacial pain and functional limitation. Although traditionally associated with adults, children and adolescents can develop TMD due to growth-related, behavioral, and psychosocial factors.
📌 Recommended Article :
Video 🔽 Massage Tutorial: Myofascial release for TMJ/jaw pain ... It is important to determine what is the cause of the TMJ syndrome, to carry out a good treatment, for this, tests such as: x-rays, occlusal analysis, magnetic resonance, etc. are carried out.Early identification and appropriate management are essential to prevent chronic pain and functional impairment during craniofacial development.
Advertisement
✅ Understanding Pediatric Temporomandibular Disorders
TMD refers to a group of conditions affecting the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), masticatory muscles, and associated structures. In pediatric patients, these disorders may present differently than in adults due to ongoing growth and neuromuscular adaptation.
Common contributing factors include:
▪️ Parafunctional habits (bruxism, nail biting)
▪️ Malocclusion or occlusal instability
▪️ Psychological stress and anxiety
▪️ Trauma or microtrauma
▪️ Growth-related joint remodeling
📌 Recommended Article :
Dental Article 🔽 Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorders: Structure, Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment ... Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders are among the most frequent causes of orofacial pain and functional limitations in dentistry. Understanding the anatomy, etiology, clinical presentation, and management of TMJ pathologies is crucial for effective patient care.✅ Clinical Evaluation of TMD in Children
A thorough clinical examination remains the cornerstone of diagnosis. The evaluation should be age-appropriate and minimally invasive.
Key diagnostic components include:
▪️ Detailed medical and dental history
▪️ Assessment of jaw pain, clicking, or locking
▪️ Measurement of mandibular range of motion
▪️ Palpation of TMJ and masticatory muscles
▪️ Evaluation of occlusion and oral habits
Imaging studies such as panoramic radiographs or MRI are reserved for persistent, severe, or progressive cases.
📌 Recommended Article :
Dental Article 🔽 Trismus: Causes, Risk Factors, Prevention, and Treatment Options ... Trismus is defined as a limitation of mouth opening, usually less than 35 mm, which interferes with eating, oral hygiene, and dental treatment. Its etiology is multifactorial, and its management often requires an interdisciplinary approach.✅ Evidence-Based Management Strategies
Current guidelines emphasize conservative and reversible treatments as first-line therapy in pediatric TMD.
Common management approaches include:
▪️ Patient and parent education
▪️ Behavioral modification and habit awareness
▪️ Physiotherapy and jaw exercises
▪️ Occlusal splints (used cautiously in growing patients)
▪️ Stress management and psychological support
Pharmacologic therapy is limited and typically restricted to short-term use of analgesics or anti-inflammatory agents.
📊 Comparative Table: Conservative Management Approaches for Pediatric TMD
| Aspect | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Patient Education | Improves compliance and habit awareness | Requires parental involvement and consistency |
| Physiotherapy | Enhances muscle function and reduces pain | Effectiveness depends on patient cooperation |
| Behavioral Therapy | Addresses stress-related contributing factors | Limited access in some clinical settings |
| Occlusal Splints | Reduces parafunctional activity and muscle overload | Must be monitored due to craniofacial growth |
| Pharmacologic Therapy | Short-term pain relief | Not suitable for long-term management |
The literature consistently supports that most pediatric TMD cases are self-limiting or respond well to conservative care. Aggressive or irreversible interventions are discouraged due to the risk of interfering with normal craniofacial growth.
Psychosocial factors play a significant role in symptom perception and persistence, highlighting the importance of a multidisciplinary approach when necessary.
✍️ Conclusion
Temporomandibular disorders in pediatric patients require early recognition and conservative management. Evidence-based evaluation and non-invasive therapies provide favorable outcomes while safeguarding normal growth and development.
📌 Recommended Article :
Dental Article 🔽 Myofascial Pain Syndrome in Dentistry: Clinical Impact and Modern Management ... Myofascial pain syndrome (MPS) is one of the most prevalent muscular causes of orofacial and jaw pain, often presenting with facial trigger points and mimicking temporomandibular joint dysfunction (TMJ disorder) or tooth pain.🔎 Clinical Recommendations
▪️ Prioritize conservative and reversible treatments
▪️ Avoid irreversible occlusal or surgical interventions in children
▪️ Educate parents and caregivers on habit control
▪️ Monitor growth and symptom progression regularly
▪️ Refer to specialists when symptoms persist or worsen
📚 References
✔ American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry. (2023). Temporomandibular disorders in children and adolescents. The Reference Manual of Pediatric Dentistry, 487–494. https://www.aapd.org/research/oral-health-policies--recommendations/temporomandibular-disorders/
✔ De Leeuw, R., & Klasser, G. D. (2018). Orofacial pain: Guidelines for assessment, diagnosis, and management (6th ed.). Quintessence Publishing.
✔ List, T., & Jensen, R. H. (2017). Temporomandibular disorders: Old ideas and new concepts. Cephalalgia, 37(7), 692–704. https://doi.org/10.1177/0333102416686302
✔ Manfredini, D., Winocur, E., Guarda-Nardini, L., Paesani, D., & Lobbezoo, F. (2011). Epidemiology of bruxism in children and adolescents. Journal of Oral Rehabilitation, 38(6), 418–429. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2842.2010.02190.x
✔ Michelotti, A., & Iodice, G. (2010). The role of orthodontics in temporomandibular disorders. Journal of Oral Rehabilitation, 37(6), 411–429. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2842.2010.02087.x
📌 More Recommended Items
► How to Reduce a TMJ Dislocation?
► Diagnosis of temporomandibular joint (TMJ) ankylosis in children
► What Are The Causes Of TMJ Related Headaches?