✅ Abstract
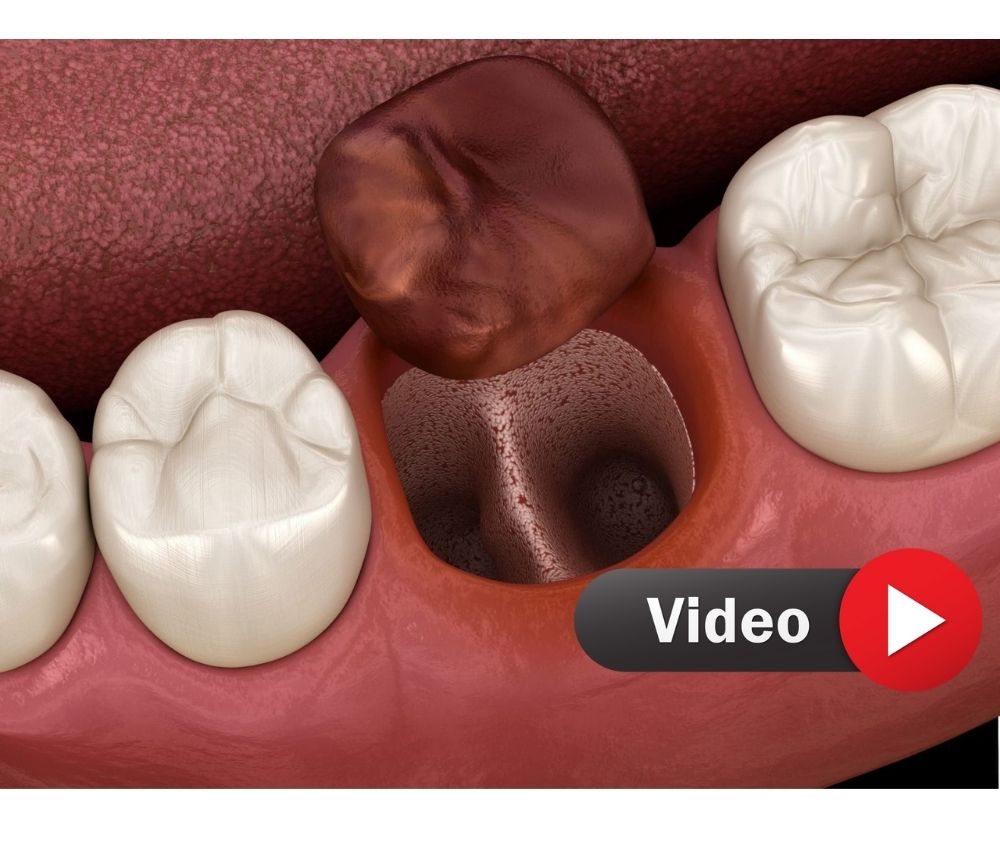
Dry socket (alveolar osteitis) is a painful post-extraction complication that can occur in pediatric dentistry, although it is more frequent in adults.
📌 Recommended Article :
Dental Article 🔽 Clinical Protocols to Prevent Dry Socket: Evidence-Based Strategies for Dental Professionals ... Dry socket is defined as the loss or disintegration of the blood clot in the extraction socket, resulting in exposed alveolar bone, radiating pain, and delayed healing.This article reviews the etiology, clinical presentation, prevention, and management of dry socket in children, focusing on current pharmacologic and clinical strategies to ensure faster recovery and prevent recurrence.
Advertisement
✅ Introduction
Tooth extraction in pediatric patients is a common dental procedure, often required due to caries, trauma, or orthodontic needs. Although usually uneventful, post-extraction complications such as dry socket (alveolar osteitis) may occasionally occur.
In children, the incidence is lower than in adults, estimated between 0.5% and 2% (Blum, 2002). Nevertheless, understanding its prevention and treatment is crucial for pediatric dentists to ensure optimal healing and patient comfort.
📌 Recommended Article :
PDF 🔽 Surgical excision of mucocele with local anesthesia in an 8-month-old baby ... The mucocele is a common cyst of the minor salivary glands, and is produced by the accumulation or retention of mucosa as a consequence of an obstruction or trauma to the salivary duct.✅ Definition and Etiology
Dry socket is defined as the premature loss or disintegration of the blood clot within the extraction socket, leading to exposure of the underlying alveolar bone. It typically manifests 24–72 hours after extraction and is associated with severe localized pain.
➤ Etiologic factors include:
▪️ Traumatic extraction techniques
▪️ Bacterial contamination
▪️ Poor oral hygiene
▪️ Premature rinsing or suction habits
▪️ Systemic conditions or medications affecting healing
Though less frequent in children due to their better vascularity and bone turnover, dry socket can still appear after difficult extractions, especially of primary molars with root resorption.
📌 Recommended Article :
Video 🔽 Tooth Extraction: Post-Surgical Care and Tips ... The professional should talk with the patient about the care that he should have to avoid complications after the surgical procedure. Some of these complications can be: bleeding or infections.✅ Clinical Signs and Symptoms
Typical features include:
▪️ Severe, throbbing pain radiating to the ear or temporal region
▪️ Empty socket with partially or completely missing clot
▪️ Exposed bone visible on inspection
▪️ Halitosis or foul taste
▪️ Localized lymphadenopathy or mild fever in rare cases
Pain usually peaks 48–72 hours post-extraction, and may last up to 7–10 days without intervention.
📌 Recommended Article :
Video 🔽 How to control bleeding after extraction? ... Post-treatment bleeding is a common complication after tooth extraction, so it is important that the dentist makes recommendations to avoid any type of problems.✅ Diagnosis
Diagnosis is clinical, based on the absence of a normal clot and the presence of exposed bone with persistent pain. Radiographic examination may be indicated to exclude retained roots or foreign bodies.
Differential diagnosis includes:
▪️ Infected socket (alveolitis suppurativa)
▪️ Osteomyelitis
▪️ Neuralgia or referred pain
📌 Recommended Article :
PDF 🔽 Manual of extraction techniques in pediatric dentistry - Step by step ... Tooth extraction is a routine treatment in the pediatric dentist's office. This procedure is performed when the tooth presents a deep caries and impossible reconstruction, fracture due to trauma, eruptive problems.✅ Management and Medication
The management of dry socket in pediatric patients focuses on pain control, disinfection, and promoting healing rather than antibiotic overuse.
1. Local Management
▪️ Gentle irrigation with warm saline or chlorhexidine 0.12%.
▪️ Topical anesthetic dressings (e.g., Alvogyl®, containing eugenol, iodoform, and butamben) to relieve pain.
▪️ Avoid curettage to prevent further trauma.
2. Systemic Management
▪️ Analgesics: Ibuprofen (10 mg/kg every 6–8 h) or Paracetamol (15 mg/kg every 6 h).
▪️ Antibiotics: Only if secondary infection is suspected; Amoxicillin or Clindamycin are commonly used.
▪️ Hydration and soft diet to promote comfort and recovery.
3. Follow-Up
▪️ Re-evaluation after 48 hours to assess healing and pain reduction.
▪️ Removal and replacement of dressing if symptoms persist.
📌 Recommended Article :
Dental Article 🔽 How to Prevent Dry Socket After Tooth Extraction: Signs, Prevention, and Treatment Guide ... Preventing dry socket is a key responsibility shared by both dental professionals and patients, involving proper surgical technique, patient education, and targeted pharmacological management.✅ Prevention in Pediatric Dentistry
Preventive strategies are the cornerstone of management:
▪️ Atraumatic extractions and gentle tissue handling.
▪️ Pre- and postoperative chlorhexidine rinses or wipes.
▪️ Avoid immediate rinsing, spitting, or straw use for 24 hours.
▪️ Educate parents about postoperative hygiene and warning signs.
▪️ Avoid smoking exposure, as it delays clot formation even in passive settings.
📊 Comparative Table: Dry Socket Prevention and Management Approaches in Pediatric Dentistry
| Aspect | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Chlorhexidine Rinses (0.12–0.2%) | Reduces bacterial load, decreases dry socket risk | Requires compliance; not suitable for very young children |
| Topical Eugenol Dressings (e.g., Alvogyl®) | Immediate pain relief, promotes healing | May cause mild irritation or allergic response |
| Atraumatic Extraction Technique | Minimizes socket trauma and clot loss | Requires clinical experience and adequate anesthesia |
| Systemic Antibiotics (Amoxicillin, Clindamycin) | Useful if infection spreads beyond socket | Should not be used routinely; risk of resistance |
Although dry socket is rare in children, its occurrence causes considerable discomfort and anxiety. Evidence-based prevention—including the use of chlorhexidine and atraumatic extraction techniques—remains the best strategy.
Recent studies suggest that topical chlorhexidine gel (0.2%) applied immediately after extraction reduces dry socket incidence by up to 60% (Hita-Iglesias et al., 2008).
When managed appropriately, complete healing is achieved within one week, with minimal complications or recurrence.
✍️ Conclusion
Dry socket remains a manageable but preventable post-extraction complication in children. A combination of preventive care, local treatment, and adequate analgesia ensures favorable healing outcomes. Pediatric dentists should focus on minimizing trauma during extraction and educating caregivers about postoperative care.
📌 Recommended Article :
Video 🔽 Tooth Extraction Aftercare Tips ... Before extracting a tooth, the dental surgeon must instruct the patient on pre and post operative care. These recommendations are intended to protect the wound and the healing process.🔎 Recommendations
▪️ Implement standard preventive protocols after every extraction.
▪️ Prefer non-traumatic techniques and adequate anesthesia.
▪️ Avoid unnecessary antibiotic prescriptions; focus on topical antisepsis.
▪️ Schedule early follow-ups to monitor healing and manage discomfort.
📚 References
✔ Blum, I. R. (2002). Contemporary views on dry socket (alveolar osteitis): A clinical appraisal of standardization, incidence, and predisposing factors in 586 cases. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology, and Endodontology, 93(4), 395–400. https://doi.org/10.1067/moe.2002.121967
✔ Hita-Iglesias, P., Torres-Lagares, D., Flores-Ruiz, R., Magallanes-Abad, N., Basallote-González, M., & Gutiérrez-Pérez, J. L. (2008). Effectiveness of chlorhexidine gel versus rinse in preventing alveolar osteitis. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 66(3), 441–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2007.09.020
✔ Kolokythas, A., Olech, E., Miloro, M., & Schlieve, T. (2010). Alveolar osteitis: A comprehensive review of concepts and controversies. International Journal of Dentistry, 2010, 249073. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/249073
✔ Kaur, A., & Singh, H. (2019). Dry socket: A review of current concepts. International Journal of Contemporary Medical Research, 6(2), B1–B4.
📌 More Recommended Items
► Pediatric Dental Emergencies: How to Face an Urgent Consultation
► Updated Antibiotic Therapy in Pediatric Dentistry: Evidence-Based Protocols for Acute Infections
► Managing Pediatric Odontogenic Infections: Diagnosis, Symptoms, and Treatment Guidelines