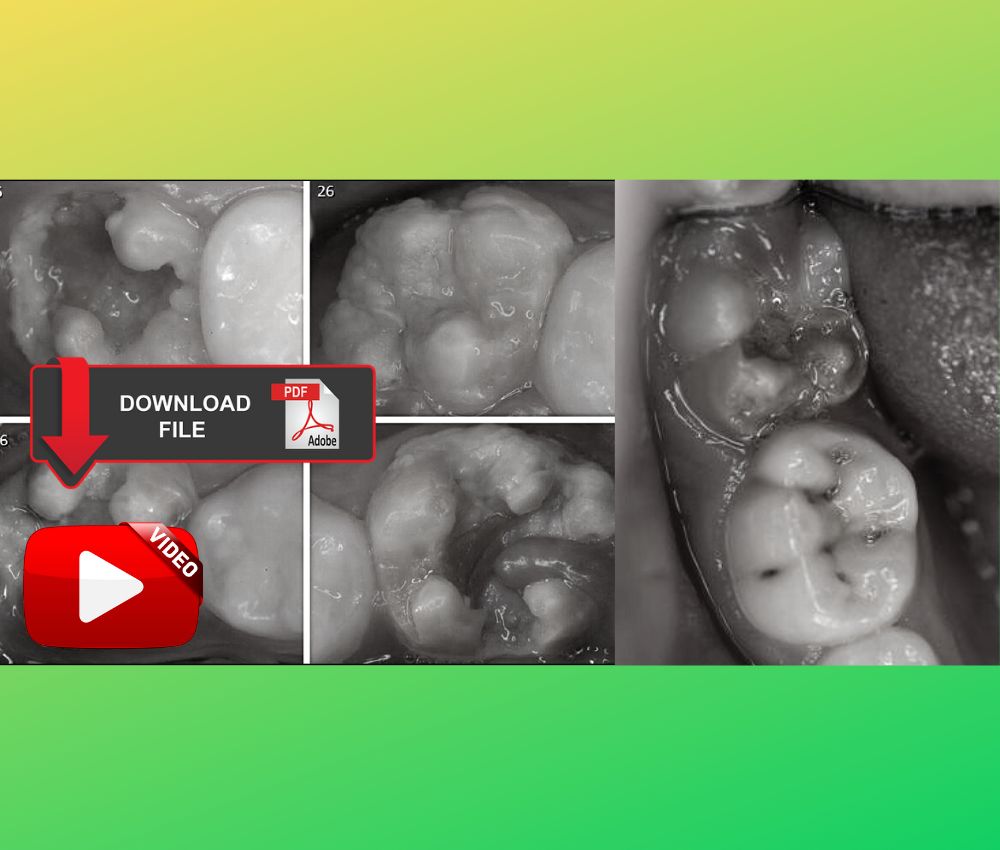
Molar–Incisor Hypomineralization (MIH) is a developmental enamel defect affecting one to four permanent first molars and often the permanent incisors.
📌 Recommended Article :
Dental Article 🔽 Enamel Hypoplasia vs Dental Fluorosis: Key Differences, Diagnosis, and Treatment ... While both conditions alter enamel structure and appearance, their etiology, presentation, and management differ significantly.Characterized by demarcated opacities, post-eruptive breakdown, hypersensitivity, and increased caries risk, MIH presents significant treatment challenges in pediatric dentistry. Early recognition and evidence-based management are essential for long-term oral health.
Advertisement
✅ Definition and Clinical Features
MIH is defined as a qualitative defect of enamel mineralization with normal enamel thickness but reduced hardness and increased porosity. Typical clinical findings include:
▪️ Demarcated opacities (white, yellow, or brown).
▪️ Post-eruptive enamel breakdown (PEB) shortly after eruption.
▪️ Severe dentin hypersensitivity, often disproportionate to clinical appearance.
▪️ High caries susceptibility due to compromised enamel structure.
▪️ Rapid restoration failure, especially in molars affected by PEB.
📌 Recommended Article :
Dental Article 🔽 Molar-Incisor Hypomineralization and Enamel Hypoplasia: Updated Clinical Approaches in Pediatric Dentistry ... Differentiating them is critical, as each condition requires a distinct diagnostic and therapeutic approach. This article presents the latest scientific evidence on their definition, etiology, diagnosis, and modern management.✅ Etiology
Although MIH’s exact cause remains multifactorial, current evidence highlights:
▪️ Prenatal and perinatal complications
▪️ Childhood respiratory diseases
▪️ Fever of early childhood
▪️ Environmental toxins (e.g., dioxins)
▪️ Genetic predisposition affecting amelogenesis
These factors disrupt ameloblast activity during mineralization of first permanent molars and incisors.
📌 Recommended Article :
PDF 🔽 Hall Technique Procedure Manual: Advantages, Disadvantages, Step-by-Step Procedure ... The Hall technique is a safe and effective procedure that prevents the advance of dental caries in primary teeth. One of its great advantages is its low cost and little prior preparation.✅ Clinical Diagnosis
Diagnosis is clinical and based on:
▪️ Demarcated opacities with clear boundaries
▪️ Opacity color indicating severity (white less than yellow-brown)
▪️ Post-eruptive breakdown
▪️ Hypersensitivity not explained by caries
▪️ Atypical restorations on newly erupted permanent molars
Early diagnosis allows prompt preventive reinforcement and staged treatment planning.
📌 Recommended Article :
Dental Article 🔽 Enamel Hypoplasia vs Molar-Incisor Hypomineralization (MIH): Diagnosis and Modern Management ... This article explores their etiology, clinical characteristics, and modern treatment options, providing a comprehensive guide for accurate diagnosis and management.✅ Management Strategies
1. Prevention and Sensitivity Control
▪️ Use 5% sodium fluoride varnish to enhance remineralization.
▪️ CPP-ACP creams reduce hypersensitivity and improve enamel integrity.
▪️ Desensitizing dentifrices with arginine or stannous fluoride may help.
2. Minimally Invasive Restorative Approaches
▪️ Resin infiltration for mild opacities on incisors.
▪️ Glass ionomer cement (GIC) as a temporary restoration in hypersensitive molars.
▪️ Fissure sealants for mild MIH without structural loss.
3. Definitive Restorative Treatment
▪️ Resin composite for moderate breakdown, though longevity is limited.
▪️ Stainless steel crowns (SSC) are the gold standard for severely affected molars, reducing sensitivity and restoring function.
▪️ Indirect restorations (e.g., onlays) in permanent dentition.
4. Extraction Planning
Early extraction of first permanent molars may be indicated in severe cases where long-term prognosis is poor, ideally between 8–10 years, considering orthodontic outcomes.
📊 Comparative Table: Differential Diagnosis of MIH
| Aspect | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Fluorosis | Symmetrical; diffuse opacities; usually no PEB | May resemble white MIH lesions; requires careful history |
| Amelogenesis Imperfecta | Generalized involvement; clear genetic pattern | Severe enamel defects may mimic MIH; affects all teeth |
💬 Discussion
MIH requires individualized care due to its wide variability in severity and patient discomfort. Restorations tend to fail more often compared to sound enamel, particularly when moisture control is compromised or hypersensitivity impedes cooperation. The use of bioactive materials, SSCs, and minimal intervention approaches has significantly improved outcomes. Long-term follow-up is essential, as MIH is a chronic condition requiring ongoing preventive support.
📌 Recommended Article :
PDF 🔽 Anterior dental esthetics in primary teeth - Oral Rehabilitation ... We share an article that evaluates the advantages and disadvantages of different aesthetic options to restore primary teeth that have been affected by extensive caries or a fracture.✍️ Conclusion
Effective management of Molar–Incisor Hypomineralization depends on early diagnosis, prevention, and appropriate restorative strategies based on severity. The integration of bioactive materials, fluoride therapies, and SSCs enhances prognosis. Clinicians must provide continuous monitoring and individualized care to reduce pain, prevent caries progression, and maintain long-term function.
🔎 Recommendations
▪️ Prioritize early diagnosis during the eruption period.
▪️ Apply high-fluoride varnish and desensitizing protocols regularly.
▪️ Use SSCs in cases of severe PEB for long-term stability.
▪️ Consider resin infiltration for aesthetic management of incisor opacities.
▪️ Evaluate orthodontic implications before extracting compromised molars.
▪️ Schedule frequent recall visits (every 3–6 months).
📚 References
✔ Alaluusua, S. (2010). Aetiology of molar–incisor hypomineralisation: A systematic review. European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry, 11(2), 53–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03262713
✔ Elhennawy, K., & Schwendicke, F. (2016). Managing molar–incisor hypomineralization: A systematic review. Journal of Dentistry, 55, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdent.2016.09.012
✔ Fagrell, T. G., Ludvigsson, J., & Lundin, S. A. (2011). Childhood illnesses and molar incisor hypomineralization. Acta Odontologica Scandinavica, 69(4), 234–244. https://doi.org/10.3109/00016357.2010.549502
✔ Weerheijm, K. L. (2003). Molar incisor hypomineralisation (MIH): Clinical presentation and management. Dental Update, 30(1), 9–12. https://doi.org/10.12968/denu.2003.30.1.9
📌 More Recommended Items
► Esthetic restoration of deciduous anterior teeth using prefabricated zirconia crowns: A case report
► ORAL REHABILITATION of a child with dentinogenesis imperfecta
► How to Diagnose and Manage MIH and Enamel Hypoplasia in Daily Dental Practice

.jpg)