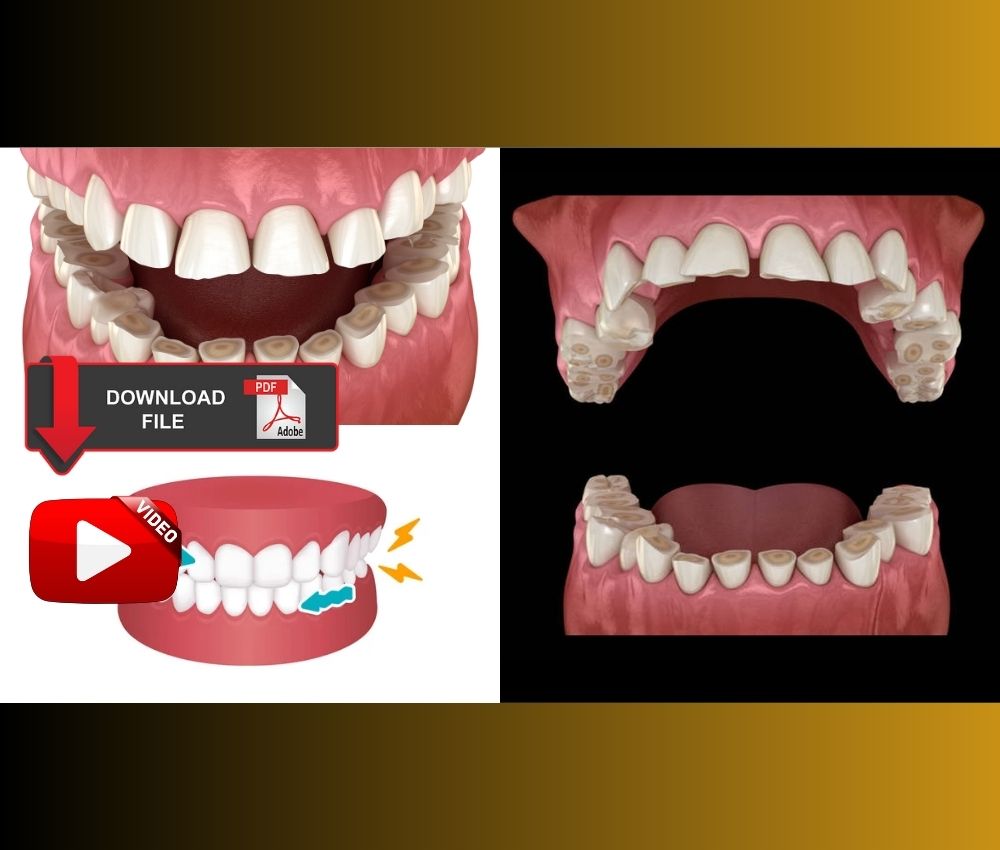
Bruxism is a common parafunctional activity characterized by involuntary clenching or grinding of teeth, occurring during sleep or wakefulness. It is associated with tooth wear, temporomandibular disorders (TMD), muscle pain, and restorative complications.
📌 Recommended Article :
Dental Article 🔽 Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Pediatric Dentistry: When and How to Use It Safely in 2025 ... Antibiotic prophylaxis in pediatric dentistry is a preventive measure used to avoid serious systemic infections, such as infective endocarditis, in children undergoing dental procedures.Current evidence indicates that bruxism has a multifactorial etiology, including central nervous system regulation, psychosocial factors, and sleep-related mechanisms.
Advertisement
Night guards (occlusal splints) are widely used in dental practice as a conservative management approach. However, it is essential to emphasize that night guards do not cure bruxism; instead, they protect oral structures and reduce the clinical consequences of excessive occlusal forces.
📌 Recommended Article :
Dental Article 🔽 Night Guards: Do They Really Help with Bruxism? ... It can occur during sleep (sleep bruxism) or while awake (awake bruxism) and is associated with tooth wear, temporomandibular disorders, and orofacial pain.✅ Understanding Bruxism: Clinical Considerations
Bruxism is classified as:
▪️ Sleep bruxism, a sleep-related movement disorder.
▪️ Awake bruxism, often associated with stress and behavioral factors.
Clinical diagnosis relies on patient history, clinical signs (wear facets, fractures), muscle tenderness, and, in selected cases, instrumental assessments. Accurate diagnosis is essential to avoid overtreatment and to select appropriate management strategies.
📌 Recommended Article :
PDF/Video 🔽 Bruxism: What are the symptoms? How is it diagnosed? ... Bruxism can occur at any age, and must be diagnosed and treated in time to avoid its serious consequences and complications. Treatment is sometimes usually multidisciplinary.✅ Role of Night Guards in Bruxism Management
Night guards act as protective and biomechanical devices, reducing direct tooth-to-tooth contact and redistributing occlusal forces. Their main clinical roles include:
▪️ Prevention of enamel wear and fractures
▪️ Reduction of muscle hyperactivity
▪️ Protection of restorations and prostheses
▪️ Symptom relief in TMD-related discomfort
Importantly, night guards do not modify the central mechanisms responsible for bruxism, reinforcing the need for patient education and realistic expectations.
📌 Recommended Article :
Video 🔽 What are the consequences of bruxism? ... In many cases, the patient does not know that he suffers from bruxism, and is detected when he attends the dentist motivated by another consultation.✅ Types of Night Guards
Commonly used appliances include:
▪️ Hard acrylic stabilization splints, typically fabricated for the maxilla
▪️ Soft or dual-laminate splints, often used for short-term protection
▪️ Anterior bite appliances, indicated in selected cases under strict monitoring
Material selection and design should be based on occlusal stability, symptom severity, and patient compliance.
📌 Recommended Article :
Video 🔽 Everything you need to know about bruxism ... The treatment of bruxism is multidisciplinary. In dentistry, discharge splints are made to relieve pain and muscle tension and prevent premature wear of the enamel.✅ Clinical Indications and Limitations
Night guards are indicated for patients with:
▪️ Moderate to severe tooth wear
▪️ Recurrent restoration failure
▪️ Muscle-related pain associated with bruxism
▪️ Temporomandibular discomfort
Limitations include:
▪️ Lack of effect on bruxism frequency
▪️ Possible occlusal changes if poorly designed or improperly monitored
▪️ Dependence on patient adherence
📌 Recommended Article :
Video 🔽 What are the symptoms of clenched teeth and how can we fix it? ... Grinding and grinding of the teeth is called bruxism. This activity is nocturnal and in states of unconsciousness. The consequences of bruxism is varied, since it affects teeth, muscles and bones.✅ Multidisciplinary Management Approach
Optimal bruxism management requires a multimodal strategy, combining:
▪️ Occlusal protection (night guards)
▪️ Behavioral counseling and stress management
▪️ Sleep hygiene optimization
▪️ Referral to medical professionals when sleep disorders are suspected
💬 Discussion
Current literature supports night guards as an effective method for damage control rather than etiologic treatment. Their value lies in preventing irreversible dental damage and improving patient comfort. Dentists must clearly communicate their protective role and integrate them into a broader management plan tailored to individual risk factors.
📌 Recommended Article :
Dental Article 🔽 Is Bruxism a Medical or Dental Problem? Causes, Risks, and Treatments ... This article explores whether it should be considered a dental problem, a medical condition, or both, by examining its signs, contributing factors, risk assessment tools, treatment strategies, and clinical management plans.✍️ Conclusion
Night guards remain a cornerstone in the conservative management of bruxism, offering significant protection against dental and muscular complications. However, they should be prescribed with a clear understanding of their limitations and supportive role within a comprehensive, evidence-based treatment strategy.
🎯 Clinical Recommendations
▪️ Perform a thorough clinical assessment before prescribing a night guard
▪️ Educate patients that night guards control consequences, not causes
▪️ Ensure regular follow-up to monitor occlusion and appliance wear
▪️ Integrate behavioral and medical interventions when indicated
📊 Comparative Table: Treatment Options for Bruxism
| Treatment Approach | Clinical Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Night Guards (Occlusal Splints) | Protect teeth and restorations; reduce muscle load; improve comfort | Do not eliminate bruxism; require patient compliance |
| Behavioral Therapy | Addresses stress-related triggers; useful in awake bruxism | Limited effect on sleep bruxism; requires long-term commitment |
| Pharmacological Management | May reduce muscle activity in selected cases | Not recommended for routine use; potential side effects |
| Physiotherapy | Improves muscle function and reduces pain | Supportive role only; does not prevent tooth wear |
✔ Lobbezoo, F., Ahlberg, J., Glaros, A. G., et al. (2018). Bruxism defined and graded: An international consensus. Journal of Oral Rehabilitation, 45(11), 837–844.
✔ Manfredini, D., Winocur, E., Guarda-Nardini, L., Paesani, D., & Lobbezoo, F. (2013). Epidemiology of bruxism in adults. Journal of Orofacial Pain, 27(2), 99–110.
✔ Klasser, G. D., & Greene, C. S. (2009). The changing field of temporomandibular disorders. Journal of the Canadian Dental Association, 75(7), 507–512.
✔ Dao, T. T. T., & Lavigne, G. J. (1998). Oral splints: The crutches for temporomandibular disorders and bruxism? Critical Reviews in Oral Biology & Medicine, 9(3), 345–361.
📌 More Recommended Items
► Night Guards for Bruxism: A Complete Dental Guide for Symptom Prevention and Control
► How Can I Tell If I Have Bruxism? A Practical Dental Guide for Patients
► How Can I Tell If I Have Bruxism? A Practical Dental Guide for Patients